Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common and often uncomfortable condition affecting millions of people worldwide. When seeking treatment, many wonder about the effectiveness of various antibiotics. Trimethoprim powder has emerged as a potential solution for managing UTIs. This blog post will explore the use of Trimethoprim powder in treating urinary tract infections, addressing key questions and providing valuable insights for those seeking information on this topic.
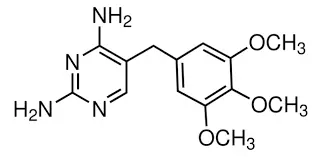
How does Trimethoprim powder work against UTI-causing bacteria?
Trimethoprim powder is an antibiotic that belongs to the class of drugs known as dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors. Its mechanism of action is particularly effective against many bacteria commonly responsible for urinary tract infections. Here's how Trimethoprim works to combat UTI-causing bacteria:
- Folate amalgamation restraint: Trimethoprim meddling with the bacterial cell's capacity to deliver folate, an fundamental component for DNA blend and cell division. By blocking the chemical dihydrofolate reductase, Trimethoprim anticipates microscopic organisms from changing over dihydrofolic corrosive to tetrahydrofolic corrosive, a vital step in folate metabolism.
- Selective poisonous quality: One of the key points of interest of Trimethoprim is its specific poisonous quality. It has a much higher liking for bacterial dihydrofolate reductase compared to the human chemical. This selectivity permits Trimethoprim to viably target bacterial cells whereas minimizing impacts on human cells.
- Broad-spectrum movement: Trimethoprim shows broad-spectrum antimicrobial movement, meaning it is successful against a wide run of microscopic organisms. This incorporates common UTI-causing pathogens such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus mirabilis.
- Concentration in pee: Trimethoprim is basically excreted through the kidneys, coming about in tall concentrations of the medicate in the urinary tract. This characteristic makes it especially successful for treating UTIs, as the anti-microbial can straightforwardly target microscopic organisms in the bladder and urinary system.
- Synergistic impacts: Trimethoprim is regularly combined with sulfamethoxazole (another anti-microbial) to make a pharmaceutical known as co-trimoxazole. This combination improves the by and large antibacterial impact by focusing on two diverse stages of the bacterial folate amalgamation pathway.
Understanding how Trimethoprim powder works against UTI-causing bacteria highlights its importance as a valuable tool in the treatment of urinary tract infections. Its targeted action, high concentration in urine, and broad-spectrum activity make it an effective choice for many patients suffering from UTIs.
What is the recommended dosage of Trimethoprim powder for UTI treatment?
Determining the appropriate dosage of Trimethoprim powder for UTI treatment is crucial for ensuring effective therapy while minimizing the risk of adverse effects. The recommended dosage can vary based on several factors, including the severity of the infection, patient age, and overall health status. Here's a comprehensive guide to Trimethoprim dosing for UTI treatment:
- Standard grown-up measurement: For most grown-ups with uncomplicated UTIs, the normal suggested dosage of Trimethoprim is 100 mg taken twice every day or 200 mg taken once every day. This regimen is more often than not proceeded for 3 to 14 days, depending on the seriousness of the contamination and the patient's reaction to treatment.
- Dosage for serious contaminations: In cases of more extreme or complicated UTIs, higher dosages may be endorsed. A few healthcare suppliers may prescribe 200 mg of Trimethoprim taken twice every day for these cases.
- Pediatric dosing: For children, the dose is ordinarily calculated based on body weight. The normal suggestion is 4 mg per kilogram of body weight per day, isolated into two measurements. This can be balanced by the pediatrician based on the child's age and the seriousness of the infection.
- Elderly patients: More seasoned grown-ups may require measurements alterations, especially if they have decreased kidney work. In such cases, a lower dosage or expanded interim between measurements might be recommended.
- Prophylactic utilize: For patients inclined to repetitive UTIs, a lower dosage of Trimethoprim may be endorsed for long-term prophylaxis. This regularly includes taking 100 mg at sleep time or 50 mg twice daily.
- Renal impedance contemplations: Patients with kidney issues may require measurements alterations. In cases of serious renal disability, the dosage might be decreased to 50 mg twice day by day or less, depending on creatinine clearance levels.
- Duration of treatment: Whereas numerous uncomplicated UTIs can be treated with a 3-day course of Trimethoprim, a few circumstances may require longer treatment. Your healthcare supplier will decide the fitting term based on your particular case.
- Timing of dosages: Trimethoprim can be taken with or without nourishment. In any case, taking it at the same times each day makes a difference keep up steady blood levels of the pharmaceutical.
It's important to note that while these guidelines provide a general framework, the exact dosage should always be determined by a healthcare professional. They will consider individual factors such as medical history, concurrent medications, and the specific characteristics of the infection.
Patients should always follow their healthcare provider's instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Completing the full course of antibiotics as prescribed is crucial, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished. This helps ensure the infection is fully cleared and reduces the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Are there any potential interactions between Trimethoprim powder and other medications?
When considering the use of Trimethoprim powder for treating urinary tract infections, it's crucial to be aware of potential drug interactions. Trimethoprim can interact with various medications, which may affect its efficacy or lead to unintended effects. Understanding these interactions is essential for safe and effective treatment. Here's an overview of potential interactions between Trimethoprim and other medications:
- Anticoagulants: Trimethoprim may improve the anticoagulant impact of drugs like warfarin. This interaction can increment the chance of dying. Patients on anticoagulant treatment may require closer checking of their INR (Worldwide Normalized Proportion) and potential measurements adjustments.
- Methotrexate: Trimethoprim can increment methotrexate levels in the body by diminishing its renal excretion. This interaction can possibly lead to methotrexate harmfulness. Patients utilizing methotrexate, frequently endorsed for conditions like rheumatoid joint pain or certain cancers, ought to be closely observed if Trimethoprim is necessary.
- Phenytoin: Trimethoprim may increment serum concentrations of phenytoin, an antiepileptic sedate. This can possibly lead to phenytoin harmfulness. Observing phenytoin levels and altering measurements may be fundamental when utilized concurrently with Trimethoprim.
- Digoxin: Trimethoprim can increment digoxin levels, especially in elderly patients or those with renal disability. This interaction may require closer observing of digoxin levels and potential measurements alterations to dodge digoxin toxicity.
- Potassium-sparing diuretics: Concurrent utilize of Trimethoprim with potassium-sparing diuretics like spironolactone or amiloride can increment the chance of hyperkalemia (tall potassium levels). This is especially imperative in patients with renal disability or those taking other drugs that can influence potassium levels.
- Cyclosporine: Trimethoprim may increment cyclosporine levels, possibly driving to nephrotoxicity. Patients on cyclosporine treatment, regularly utilized in organ transplant beneficiaries, ought to be observed closely if Trimethoprim is prescribed.
- Oral hypoglycemics: There have been reports of improved hypoglycemic impacts when Trimethoprim is utilized concurrently with a few verbal diabetes solutions. Blood glucose levels ought to be observed more closely in diabetic patients beginning Trimethoprim therapy.
- Dofetilide: The combination of Trimethoprim and dofetilide, an antiarrhythmic medicine, is for the most part contraindicated due to the potential for genuine cardiac arrhythmias.
- Lamivudine: Trimethoprim may increment lamivudine levels, an antiretroviral sedate utilized in HIV treatment. Whereas this interaction is by and large not clinically critical, mindfulness is vital, particularly in patients with renal impedance.
It's important to note that this list is not exhaustive, and new interactions may be discovered over time. Healthcare providers should always review a patient's complete medication list before prescribing Trimethoprim. Patients should inform their healthcare providers about all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins.
In some cases, the benefits of using Trimethoprim may outweigh the risks of potential interactions. Healthcare providers may choose to prescribe Trimethoprim while implementing additional monitoring or making dose adjustments to other medications. In other situations, alternative antibiotics may be considered to avoid significant drug interactions.
Patients should never adjust their medication regimen without consulting their healthcare provider. If any unusual symptoms or side effects occur while taking Trimethoprim in combination with other medications, it's crucial to seek medical advice promptly.
By being aware of these potential interactions and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, patients can ensure the safe and effective use of Trimethoprim powder for treating urinary tract infections while minimizing the risk of adverse drug interactions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Trimethoprim powder can be an effective treatment for urinary tract infections when used appropriately. Its mechanism of action, targeted efficacy against UTI-causing bacteria, and ability to concentrate in the urinary tract make it a valuable option for many patients. However, as with any medication, it's crucial to use Trimethoprim under the guidance of a healthcare professional, adhering to recommended dosages and being aware of potential drug interactions. By understanding how Trimethoprim works, following proper dosing guidelines, and being vigilant about potential interactions with other medications, patients can maximize the benefits of this antibiotic while minimizing risks. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment plans tailored to your specific health needs and medical history. If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact lea_slsbio@163.com,WhatsApp+86 13193326505.

References
1. Gupta K, et al. (2011). International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 52(5), e103-e120.
2. Hitchings GH. (1973). Mechanism of action of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 128(Supplement 3), S433-S436.
3. Masters PA, et al. (2003). Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole revisited. Archives of Internal Medicine, 163(4), 402-410.
4. Milo G, et al. (2005). Duration of antibacterial treatment for uncomplicated urinary tract infection in women. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (2).
5. Nahata MC, et al. (1982). Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole dosage for infants and children. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 22(1), 145-150.
6. Nguyen HM, et al. (2019). Update on the management of urinary tract infections in the era of antimicrobial resistance. Postgraduate Medicine, 131(1), 32-41.

